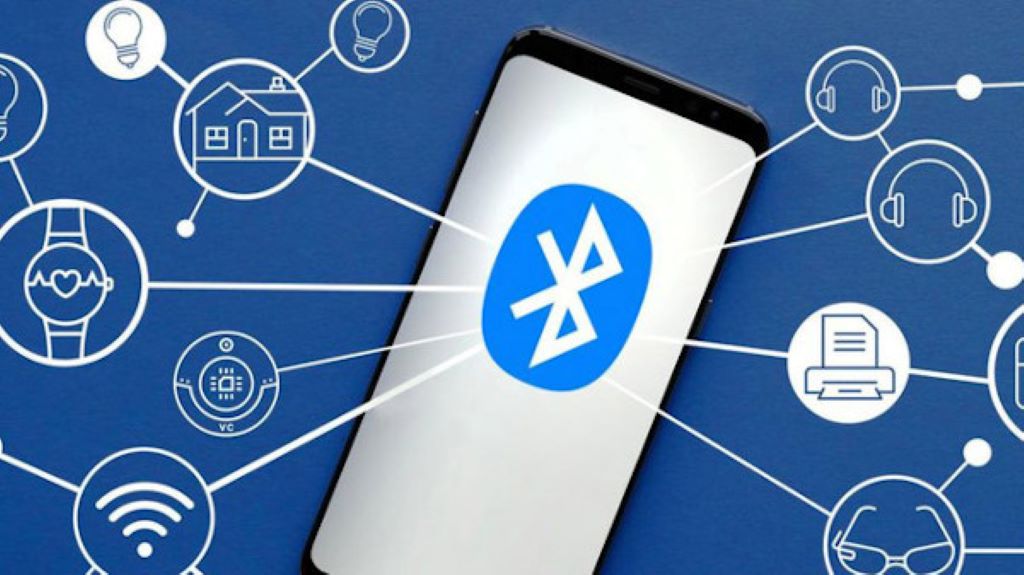
Bluetooth technology has become an indispensable component of our daily lives, providing us with the convenience of wireless connectivity to a diverse range of devices. Bluetooth has revolutionized how we interact with technology, from wireless headphones and speakers to smart home appliances, fitness trackers, and even vehicles. Over the last two decades, Bluetooth has become a ubiquitous technology that enables seamless communication, data transfer, and access to information, making life easier and more efficient for millions of people worldwide. It has eliminated the need for cords, cables, and wires, allowing for greater freedom of movement and enhanced user experience. With Bluetooth, we can connect and control multiple devices simultaneously, stream music, share files, and much more with just a few clicks or taps. The impact of Bluetooth on modern life is undeniable, and it is hard to imagine a world without this versatile and game-changing technology. Let’s look at Bluetooth’s origins, how has Bluetooth impacted society today, the different versions over the years, and the many ways it has impacted society.
A Brief History of Bluetooth

Bluetooth began in 1994 when Ericsson, a Swedish telecommunications company, started researching ways for mobile phones to communicate with each other and with computers. In 1998, Ericsson joined forces with Intel, IBM, Toshiba, and Nokia to form the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) to develop standards for short-range wireless connectivity.
The name “Bluetooth” comes from Harald Blåtand, a 10th-century Scandinavian king who united Denmark and Norway. The implication was that Bluetooth technology would join devices like this ancient king, who united differing nations.
The first Bluetooth specification was released in 1999, allowing connectivity within a range of 10 meters. This was extended to 100 meters in the updated 1.2 specification released in 2003. Over the years, the SIG has updated Bluetooth standards for faster data transfer speeds and enhanced capabilities.
How Does Bluetooth Work?
Bluetooth uses short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the industrial, scientific, and medical radio bands between 2402 and 2480 MHz to transmit data wirelessly over short distances.
Bluetooth communication has two main components: the controller and agent devices. The controller device initiates and controls the connection by sending signals and determining frequency hopping patterns. Meanwhile, the agent device synchronizes with the master’s address and clock, staying locked to the controller device’s phase and frequency hopping sequence.
Bluetooth uses spread spectrum frequency hopping, meaning the transmitter switches frequencies up to 1600 times per second across 79 designated Bluetooth channels to avoid interference. Bluetooth will hop over if a particular band is already in use. This adaptive frequency hopping allows Bluetooth to minimize interference with other wireless technologies sharing its spectrum.
Bluetooth Versions and Capabilities Over the Years
Bluetooth has steadily evolved over the past two decades with significant updates that expand functionality and speed. Here’s an overview of the different Bluetooth versions and their notable features:
Bluetooth 1.0 and 1.0B
- Released in 1999.
- Allowed data transfers up to 1 Mbps.
- Introduced many essential features like voice dialing and data transfers between devices.
Bluetooth 1.1
- Released in 2001.
- Improved cross-compatibility for authentication and encryption.
- She introduced faster connection speeds.
Bluetooth 1.2
- Released in 2003.
- I increased the data rate to 1 Mbps.
- Extended range up to 10-100 meters.
- She introduced adaptive frequency hopping for increased wireless coexistence.
Bluetooth 2.0 + EDR
- Released in 2004.
- Introduced Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) for faster data transfers up to 3 Mbps.
- We have improved audio quality for Bluetooth headsets.
Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR
- Released in 2007.
- Increased data transfer speeds up to 24 Mbps with EDR.
- She introduced extended inquiry responses for better device discovery.
- We have provided enhanced security with encryption critical lengths up to 128 bits.
Bluetooth 3.0 + HS
- Released in 2009.
- She introduced high-speed capabilities up to 24 Mbps.
- It allowed faster application switching with alternate MAC/PHY.
- I added unicast connectionless data support.
Bluetooth 4.0 + LE
- Released in 2010.
- She introduced Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) protocol stack for low power consumption.
- It has enabled a wide range of new IoT and smart device applications.
Bluetooth 4.1
- Released in 2013.
- It allowed role-switching between enslaver and agent devices.
- Improved speed, reliability, and power consumption.
Bluetooth 4.2
- Released in 2014.
- Increased LE data rate to 1 Mbps.
- Added compatibility for IPv6 over LE.
Bluetooth 5
- Released in 2016.
- It increased data broadcasting capacity up to 2x speed.
- Extended range up to 240m using LE-coded PHY.
Bluetooth 5.1
- Released in 2019.
- It improved audio sharing by enabling broadcast audio.
- Added functionality for High Duty Cycle Non-Connectable Advertising.
Bluetooth 5.2
- Released in 2020.
- Focuses on improving audio quality with LE Audio.
- I doubled the speed to 2 Mbps with LE 2M PHY.
- Increased robustness with Angle of Arrival and Angle of Departure measurements.
As you can see, Bluetooth capabilities have evolved immensely, allowing faster data transfers, improved power consumption, extended wireless range, enhanced audio, and advanced IoT applications. The Bluetooth SIG continues to innovate Bluetooth standards to meet the connectivity demands of the future.
Ways Bluetooth Has Impacted Society
Now that we’ve covered a brief history and technical overview let’s examine some significant ways Bluetooth technology has impacted daily life in modern society.
1. Wireless Audio
One of the most popular Bluetooth applications is wireless audio. Bluetooth headsets and headphones have made listening to music and taking calls much more convenient and cordless. Transferring audio streams over Bluetooth has enabled incredible growth in wearables and wearables.
Bluetooth is also used widely in speakers, soundbars, car audio systems, hearing aids, and other audio electronics, allowing reliable wireless audio connectivity. Streaming audio content wirelessly over Bluetooth has fundamentally changed the portable audio industry.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) has been a game changer for IoT and smart home devices. It allows for ultra-low power consumption so that devices can run for months or years on small batteries. LE enabled the explosion in IoT by facilitating communication between sensors, smart devices, and hubs across homes and buildings.
Smart home products like bright lights, thermostats, security systems, and appliances rely on Bluetooth LE to operate efficiently without wires or WiFi. This has led to greater home automation, convenience, and energy savings. Beyond the smart home, LE enables new IoT use cases across industrial, medical, fitness, and entertainment sectors.
3. Wearable Tech
Bluetooth has enabled the rise of wearables by allowing small sensors and devices to pair with smartphones for data synchronization. From smartwatches and fitness bands to AR/VR headsets and health monitoring devices, most wearables leverage Bluetooth to connect and transmit data to other devices wirelessly. This allows for smaller form factors and greater portability.
Bluetooth keeps wearables power efficient, allowing them to continuously collect and share data with apps without draining batteries. As wearables become more sophisticated, Bluetooth will play a key role in their continued evolution and adoption.
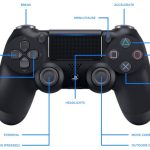
4. Wireless Gaming
Bluetooth has revolutionized wireless gaming by enabling cordless controllers, keyboards, mice, and headsets. This allows gamers to play games on computers, mobile devices, AR/VR headsets, and consoles without worrying about cables.
Wireless Bluetooth connections have made gaming with groups more convenient and comfortable. Gaming peripherals utilizing Bluetooth provide freedom of movement, are easier to transport, and reduce clutter. Bluetooth interactivity and responsiveness have greatly enhanced many gaming experiences.
5. Wireless Connectivity Everywhere
Bluetooth has become a ubiquitous wireless standard integrated into billions of devices. It provides effortless connectivity between smartphones, computers, vehicles, and electronics automatically once paired. Bluetooth facilitates wireless communication between devices nearby virtually everywhere.
BT in smartphones allows people to use wireless headsets, sync contacts, transfer files, stream music, and connect with Bluetooth devices seamlessly. Bluetooth in cars enables hands-free calling, music streaming, and GPS navigation. The prevalence of Bluetooth makes advanced connectivity readily accessible.
6. Improved Safety
Bluetooth has also improved safety across many domains. Bluetooth headsets allow for hands-free communication while driving to reduce distractions. The BT sensors can identify passenger presence and improve airbag safety. It also enables real-time alerts for workers in hazardous environments.
Doctors can monitor patients wirelessly via Bluetooth medical devices. Bluetooth beacons provide location services and navigation assistance for the visually impaired. It has even enabled tracking of luggage and essential items to prevent loss. The applications of Bluetooth for improving safety are vast.
7. Automotive Innovation
The automotive industry has embraced Bluetooth technology in modern vehicles. Bluetooth car kits enable drivers to use cell phones hands-free for calls and music. BT OBDII adapters allow monitoring of engine diagnostics. Bluetooth GPS trackers help recover stolen vehicles.
Keyless entry systems and Bluetooth Low Energy Vehicle Access promote convenience by turning smartphones into digital car keys. Cars are becoming mobile hubs, with Bluetooth facilitating communication between vehicles, passengers, and infrastructure. Bluetooth is driving meaningful automotive innovation.
8. Payment Processing
Bluetooth has become integral for cashless transactions and payment processing. Bluetooth credit card readers allow businesses to accept payments anywhere securely from smartphones and tablets. Device-to-device Bluetooth payments enable customers to pay using their mobile phones.
Bluetooth Low Energy beacons placed in stores enable contactless checkout and targeted promotions to shoppers in proximity. The speed and security of Bluetooth is helping drive the adoption of cashless payment technology globally.
9. Data Management
Bluetooth data transfer has enabled seamless data exchange between devices for business professionals and consumers. It provides cable-free synchronization of contacts, calendars, documents, photos, and files across smartphones, computers, tablets, and the cloud.
For enterprises, Bluetooth helps connect employees securely to company networks, printers, keyboards, mice, and other peripherals. Bluetooth technology is making data management and accessibility more wireless.
10. Location Based Services
Bluetooth beacons and proximity solutions have opened up new location-based capabilities. Retailers use Bluetooth beacons to detect customer movements and provide navigation, promotions, or product information. Logistics firms use Bluetooth tags to track assets end-to-end across facilities.
Airports have installed Bluetooth beacons to provide visually impaired travelers audio guidance to gates and services. The applications for Bluetooth location services are far-reaching across sectors.

The Future of Bluetooth
As you can see, Bluetooth has permeated many aspects of modern life. It has established itself as the de facto short-range wireless standard across consumer electronics and computing globally. There are over 4.6 billion active Bluetooth devices worldwide as of 2024. Bluetooth adoption is expected to grow exponentially with the launch of Bluetooth LE Audio and new standards to improve audio quality, coexistence, and power efficiency.
Upcoming trends like spatial audio, wearables, and an increased focus on privacy and localization indicate Bluetooth will continue innovating human-technology interfaces. The proliferation of the Internet of Things and connected devices will be another driving factor as more objects become wireless.
Bluetooth technology has plenty of untapped potential, with expanding applications in healthcare, retail, manufacturing, entertainment, and more. It remains well-positioned to provide the wireless framework enabling the technologies, environments, and experiences of the future. Two decades after its creation, Bluetooth remains an integral force shaping society.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the advantages of Bluetooth compared to other wireless technologies?
Bluetooth offers several key advantages:
- Low power consumption: Bluetooth is designed to be power efficient, making it ideal for battery-powered devices.
- Omnidirectional signal: Bluetooth uses an omnidirectional signal that can transmit in all directions, allowing more mobility.
- Built-in security: Bluetooth has built-in encryption and authentication for secure connections.
- Low cost: Bluetooth chips and software are inexpensive to implement.
- Ubiquity: Bluetooth is globally available in billions of devices.
- Ease of use: Bluetooth devices connect automatically and instantaneously when in proximity.
What are the different Bluetooth classes, and what is the range of each?
There are three main Bluetooth classes:
- Class 1: Offers a range up to 300 feet with max transmit power of 100mW. They are used primarily in industrial use cases.
- Class 2: Offers a range of up to 30 feet with a max transmit power of 2.5 mW. They are used in most consumer devices.
- Class 3: Offers a range of up to 3 feet with max transmit power of 1mW. They are used in very low-power applications.
How is Bluetooth different from WiFi? Which is better?
Bluetooth and WiFi both enable wireless communication but serve different purposes:
- Bluetooth is designed for short-range connections, while WiFi offers longer-range coverage.
- Bluetooth enables device-to-device communication, while WiFi allows devices to connect to a wireless network.
- Bluetooth connections are instant when devices are close, while WiFi requires manually joining networks.
- Bluetooth uses less power, making it better for small battery-powered devices. WiFi consumes more power but offers faster multi-user connections.
Determining whether Bluetooth or WiFi is better depends on the specific use case. They complement each other in connected ecosystems.
Can Bluetooth get hacked, and how can you stay secure?
Like all wireless signals, Bluetooth is susceptible to certain security risks if not used properly. To stay secure:
- Only pair with trusted devices; don’t allow your phone to remain discoverable.
- Disable Bluetooth when not in use and avoid using open public hotspots.
- Make sure your Bluetooth device has the latest firmware/OS updates enabled.
- Use Bluetooth solid passwords that are hard to crack.
- Employ end-to-end Bluetooth encryption for sensitive data transfers.
Does Bluetooth have adverse health risks?
Decades of research have found no proven short or long-term health risks from Bluetooth exposure. Bluetooth uses low-power radio signals that do not have enough energy to cause thermal damage to human tissue or DNA, like ionizing radiation can. However, it is still recommended to use headsets or limit exposure when feasible as a precaution.
How easy is it for someone to hack my phone via Bluetooth?
Hacking a phone via Bluetooth is difficult but possible in rare circumstances. An attacker would need to extend proximity to the target device while it’s in discoverable mode. Users should turn off Bluetooth functionality when not required and avoid using discoverable mode in public places to remain secure. Employing device encryption adds another layer of protection.
In Summary
Bluetooth has evolved from a niche short-range wireless standard in the 1990s to an integral connectivity solution across industries. It has pushed innovation in wireless audio, IoT, wearables, gaming, automotive, payments, data management, location services and more. Bluetooth offers productivity, convenience, and cutting-edge capabilities that are impossible with wires.
While some minor security and health concerns exist, Bluetooth remains a secure and low-risk technology that meets international standards. Addressing the issue of voice messages not working on iPhone through solutions and troubleshooting tips not only restores essential communication functionalities but also, by editing and enhancing the initial computer-generated text, maximizes accuracy. This right approach, similar to AI image captioning, saves immense time and makes visual content significantly more readable and impactful.